Chemical accident called a large release of emergency chemically hazardous substances (HAS) – chlorine, ammonia, hydrocyanic acid and others, which can harm the life and health of people, pollute the soil and water bodies.
There is a possibility of such an incident in any production facility that uses hazardous reagents. Problems can arise due to damage to the pipeline or storage facility, as well as during the transportation of goods. So it is better to know in advance what to do in case of an accident.
Who should prepare for a chemical accident and how to do it
Find out if there are production facilities with large reserves of chlorine, ammonia, hydrocyanic acid, phosgene, or sulfur dioxide near your place of residence or work. This can be:
- chemical, pulp and paper and processing plants;
- mineral fertilizer plants;
- production of ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy;
- cold storage plants;
- breweries;
- confectionery factories;
- vegetable warehouses;
- water stations.
If there is something similar nearby, just in case, purchase personal protective equipment (PPE) for the respiratory system – a civil gas mask or a gas-protective respirator. For example, RPG-67.
Before purchasing, make sure that the product you choose is suitable for protection against hazardous chemicals. Read the description and look for whether the filter of the selected PPE can handle, for example, chlorine or ammonia vapors.
What to buy
What to do if a chemical accident occurs
If this happens, you will hear the public alert signal “Attention everyone!” – the howl of a siren. The enterprise responsible for the emergency should also sound intermittent beeps.
Get home as soon as possible, turn on the radio or TV: information about the accident and recommended actions will be transmitted through these means of communication. You may also receive an SMS message from the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
To ensure safety, do the following:
- Close the windows, turn off electrical appliances and gas.
- Get respiratory protection. If they are not available, take available fabric items soaked in water. To protect against chlorine, the bandage should be soaked in a 2-5% solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per glass of water); from ammonia – in a 2% solution of citric or acetic acid.
- Wear thick fabric with long sleeves and long legs, gloves, rubber boots or other closed, tight shoes.
- Take your pets.
- Take your documents with you.
- If you think that your neighbors may not have heard the siren or missed the message about the accident, notify them about it.
- Help those who cannot do it themselves evacuate.
If you remain in an infested area, tightly close windows and doors, vents and chimneys. Seal the gaps with paper or tape. Some chemicals are heavier than air – for example, chlorine or hydrogen sulfide will permeate in basements and lower floors of buildings. Therefore, try to take refuge with neighbors higher up.
If during the accident you find yourself far from your home and no one needs help there, evacuate immediately. Quickly, but don’t panic go away from the area of possible infection.
Move perpendicular to the direction of the wind and do not stop until you are at least 1.5 kilometers away from your previous location. It’s about a 15-20 minute walk.
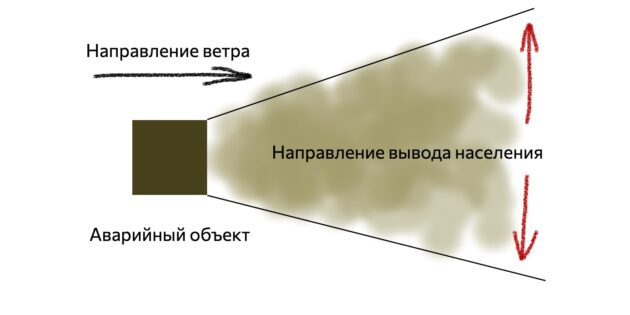
During evacuation, try not to lean against buildings or touch objects, and do not step on puddles of liquid or powder along the way. Listen to the radio on the way: they can tell you where it will be safer now and when you can return back.
How to understand that you are in the area where hazardous chemicals are spread
In addition to official data, you can be guided by your feelings. You are most likely at risk if:
1. A sharp, unusual odor appeared. You may smell a strong odor of bleach or cat urine (ammonia), bitter almonds (hydrocyanic acid), rotten eggs (hydrogen sulfide), rotten fruit, rotten leaves, or wet hay (phosgene).
The smell won’t necessarily be exactly as described, but if it’s strong and has no obvious cause, it’s a reason to be wary.
2. You see how the broken container “smoke”. This can be observed right at the scene of an accident, for example if a chlorine tank was damaged during transportation. You cannot approach such objects closer than 200 meters, so try to leave the danger zone as quickly as possible.
3. You have symptoms of poisoning. For poisoning with chemicals indicate the following signs:
- pain and pain in the eyes, lacrimation;
- sore throat, cough;
- suffocation;
- cardiopalmus;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- confusion;
- feeling of chest compression;
- metallic taste in the mouth.
If you feel something like this, try to leave the infected area as soon as possible.
What to do in case of poisoning with hazardous substances
If you or another person becomes poisoned by chemicals, the first step is to stop exposure. That is, go a sufficient distance from the source of danger or, if this is not possible, lock yourself at home and seal the room.
Call an ambulance while you wait for help, do following:
- Remove all clothing and place it in a sealed bag. Later you can wash it or throw it away.
- Take a shower and thoroughly wash with soap any areas of your body that were not protected by clothing. Rinse your mouth.
- If you feel a burning sensation in your eyes, rinse them with a 1% boric acid solution. You can also drip two drops of a 1% solution of novocaine.
- Prepare a large, warm drink, such as tea or milk.
- Provide peace and warmth until the ambulance arrives.
Until official notification that the danger has passed, refrain from drinking tap water.
If you live in a private sector, do not eat fruits and vegetables from the garden, meat of livestock and poultry slaughtered after an accident, until a conclusion has been made about their suitability for food.
Read also 🐺☢️🆘
